Physics Definition Of Impulse ~ Indeed lately is being sought by consumers around us, maybe one of you. Individuals are now accustomed to using the net in gadgets to view video and image data for inspiration, and according to the name of the article I will discuss about Physics Definition Of Impulse. Therefore impulse as defined in the previous paragraph is simply equivalent to p. Since force is a vector quantity impulse is also a vector quantity. Force is a vector quantity the direction matters and impulse is also a vector in the same direction. Impulse or change in momentum equals the average net external force multiplied by the time this force acts. Therefore the impulse does as well. Impulse or change in momentum equals the average net external force multiplied by the time this force acts. It is however possible to find an average effective force f eff that produces the same result as the corresponding time varying force. In calculus terms the impulse can be calculated as the integral of force with respect to time. We are giving a detailed and clear sheet on all physics notes that are very useful to understand the basic physics concepts. The product of impulsive force and time for which it acts is called impulse. Impulse applied to an object produces an equivalent vector change in its linear momentum also in the same direction. Note that this is a vector equation because the force has a direction. The symbol for impulse is j or imp. Forces vary considerably even during the brief time intervals considered. If a force is applied on a body for an interval of time then the product of that force and time is called impulse acted on that body. The quantity of impulse is force time interval or in shorthand notation. Forces are usually not constant. Our definition of impulse includes an assumption that the force is constant over the time interval δt. A sudden wish or urge that prompts an unpremeditated act or feeling. Impulse f t.
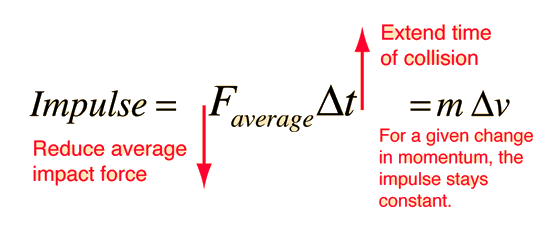
Impulse is defined in classical mechanics as a force multiplied by the amount of time it acts over. The quantity of impulse is force time interval or in shorthand notation. Force is a vector quantity the direction matters and impulse is also a vector in the same direction. If you re looking for Physics Definition Of Impulse you've reached the ideal place. We ve got 12 graphics about physics definition of impulse adding pictures, pictures, photos, wallpapers, and much more. In these web page, we additionally provide number of graphics available. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, blackandwhite, translucent, etc.
In calculus terms the impulse can be calculated as the integral of force with respect to time.
The quantity of impulse is force time interval or in shorthand notation. The motion produced by such a force. In classical mechanics impulse symbolized by or imp is the integral of a force over the time interval for which it acts. Our definition of impulse includes an assumption that the force is constant over the time interval δt.